Paleoenvironments shaped the exchange of terrestrial vertebrates across Wallace’s Line
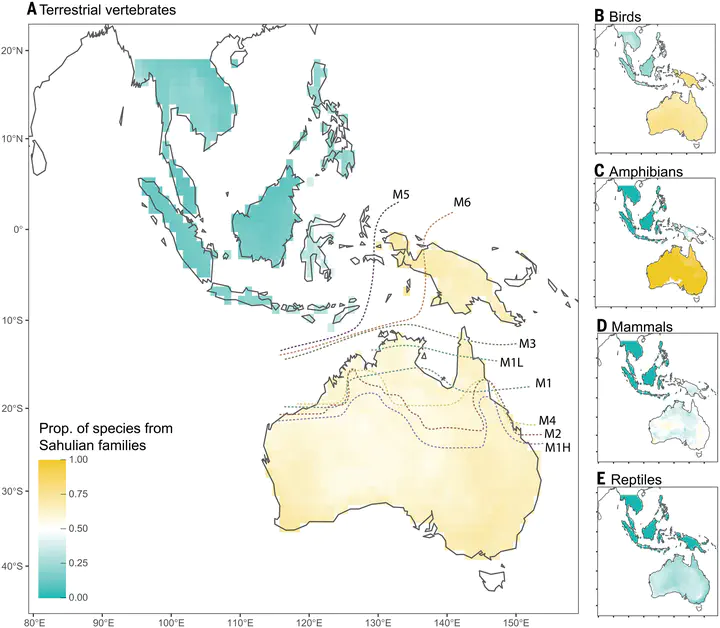 Spatial distribution of the proportion of terrestrial vertebrate species of Sahul origin and biogeographic turnover predictions from the biodiversity simulation model.
Spatial distribution of the proportion of terrestrial vertebrate species of Sahul origin and biogeographic turnover predictions from the biodiversity simulation model.
Abstract
Faunal turnover in Indo-Australia across Wallace’s Line is one of the most recognizable patterns in biogeography and has catalyzed debate about the role of evolutionary and geoclimatic history in biotic interchanges. Here, analysis of more than 20,000 vertebrate species with a model of geoclimate and biological diversification shows that broad precipitation tolerance and dispersal ability were key for exchange across the deep-time precipitation gradient spanning the region. Sundanian (Southeast Asian) lineages evolved in a climate similar to the humid “stepping stones” of Wallacea, facilitating colonization of the Sahulian (Australian) continental shelf. By contrast, Sahulian lineages predominantly evolved in drier conditions, hampering establishment in Sunda and shaping faunal distinctiveness. We demonstrate how the history of adaptation to past environmental conditions shapes asymmetrical colonization and global biogeographic structure.